Freshman Studies is an important piece of the Lawrence experience, and the required reading list is an important part of Freshman Studies.
With all first-year Lawrence University students taking Freshman Studies during their first two terms, and all sessions using the same reading list, students join together in a larger intellectual community, one that ties them not only to their fellow students across campus but also to Lawrentians from generations past.
Since its establishment in 1945, the Freshman Studies syllabus has been continuously revised to introduce a changing student body to the intellectual challenges of a liberal arts education, and to the resulting benefits of the interdisciplinary thinking it embraces. The coming academic year’s syllabus demonstrates the evolution of this ongoing task.
Learn a little more about Freshman Studies here.
We asked Garth Bond, associate professor of English and director of Freshman Studies, to guide us through the 2019-20 reading list.
Fall term
Natasha Trethewey, Native Guard. This short collection of Pulitzer Prize-winning poetry teaches students to recognize the fullness and precision of meaning in language. Trethewey’s poems meditate on the role that objects — photographs, monuments, diaries — play in shaping our memories and histories. She begins with the personal tragedy of her mother’s murder, then turns to the public history of American racism and the memorialization of the Civil War. The final section revisits personal experience, now reshaped in the light of that public history. All in 75 pages. (Adopted Fall 2015)
Thomas Seeley, Honeybee Democracy. From Trethewey’s poetic reflection on ants making a home on her mother’s grave, students move to a biologist’s study of the most fascinating of social insects: the honeybee swarm. Seeley demonstrates how our understanding of honeybees’ complex communication and social decision-making has developed systematically through the application of the scientific method; but he also reveals the benefits of interdisciplinary thinking by exploring the lessons that honeybee decision-making may have as a model both for human democratic processes and for emerging systems of artificial intelligence. (Adopted Winter 2019)
Marilynne Robinson, Housekeeping. The story of two young women growing up under the housekeeping of a series of female relatives following the death of their mother, Robinson’s novel revisits the themes of loss and memory raised by Trethewey while also exploring the human individuality—some of it troubling—that questions the lessons Seeley would draw from the more naturally communal honeybees. Robinson particularly illuminates the impact of unwritten social expectations on women who fail to conform to them, while her unreliable narrator forces students to rethink their initial views of the relationship between society and the individual in the novel. (Adopted Fall 2018)
Plato, The Republic. On the Freshman Studies syllabus since its creation in 1945, Plato’s philosophical consideration of what makes a virtuous individual and political order embodies the practice of liberal education. After discussing the proper nature of philosophical discourse, Socrates develops his arguments in dialogue with his fellows. He poses hard questions about the nature of reality and the potential dangers of democracy that challenge students’ assumptions. Our discussion of these ideas brings current students into a conversation with alumni reaching back over 70 years now, literally embodying the community-building goals of the liberal arts. (Adopted 1945).
Pieter Bruegel the Elder, Landscape with the Fall of Icarus. Bruegel’s 16th century painting, which places the mythical Icarus’s tragic crash — having flown too close to the sun — quietly in the background of a contemporary rural landscape, reminds students that images impose the same demands on our attention as poetry, narrative, and scientific or philosophical discourse. It too asks questions about the nature of loss and memory, and of the relationship between the individual and society, but posed in the “language” of images rather than words, helping students to develop the visual literacy required in our increasingly visual culture. (Adopted Fall 2016)
Winter term
The Bhagavad Gita. Having closed the Fall Term with examples of ancient and early modern Western thought, Winter opens by turning to other ancient and medieval traditions. Roughly contemporary with The Republic, this seminal Hindu scripture offers its own account of the good life, one focused on fulfilling one’s duty (or dharma) without attachment to the fruits of one’s actions. Its more poetic philosophical approach offers a probing challenge to the individualism often seen as central to Western thought. (Adopted Winter 2015)
The Arabian Nights. This 14th century collection of traditional Arabian stories forces students to consider the very nature and purpose of storytelling. As a new bride weaves tales each evening to keep her husband and king from killing her in the morning, as he has sworn to do with all of his wives, questions arise about the nature and purposes of storytelling: its relationship to power and to erotic desire, the ulterior motives governing its rhetoric, and the invasive and irresistible pull of curiosity. Far from turning away, this text revels in the fruits of human action, both ripe and rotten. (Adopted Winter 2018)
Tony Kushner, Angels in America. Set in Reagan-era Washington, D.C., this Pulitzer Prize-winning play echoes a number of the magical elements found in The Arabian Nights, but within a realistic depiction of the political and ethical conflicts of the AIDS epidemic emerging especially in the gay community at that time. While the politically diverse characters of Kushner’s script already demand careful attention to the motives and meanings of their actions, recorded versions of different productions allow students to think about the creative acts needed to move from the written page to embodied performance. (Adopted Winter 2020)
Abhijit Banerjee and Esther Duflo, Poor Economics. Moving from the historical AIDS epidemic to the contemporary battle with global poverty, two developmental economists offer a scientific approach to human action. They advocate putting aside big ideas, like increasing aid or freeing markets, in favor of careful research addressed to small, specific questions. Students see how answering these small questions can also give voice to the human experience of those living on $1 a day. Can narrowly focused action, guided by the scientific method, really outperform our political beliefs and create a quiet revolution in economic and political institutions? (Adopted Winter 2017)
Miles Davis, Kind of Blue. Lawrence’s Conservatory of Music is a fundamental part of our university community. This most famous of albums invites all students to explore the complex relationship between planned structure and improvised action at the heart of jazz performance. As a relatively early and deeply influential LP, it further challenges students to think about the processes of memory and meaning at work in permanently recording and revisiting a “live” improvisation, as well as the cultural role and context of jazz music, especially its relationship to African-American identity. (Adopted Winter 2016)
Note to incoming freshmen: Looking for your Freshman Studies books? Domestic students should receive the first book, Native Guard, in late July or early August. International students will receive the book when they arrive on campus. Students also may visit the online bookstore, www.lawrence.edu/academics/bookstore. Be aware, though, that Freshman Studies sections won’t appear in the bookstore (or on student schedules) until those sections have been created in mid-August.
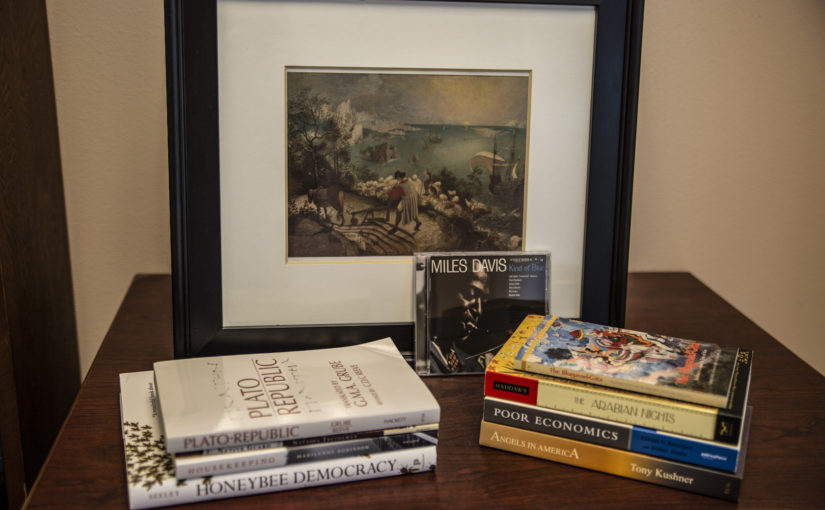





 Taking a page from Freshman Studies, Green Roots is sponsoring a special 1-unit course for Term III under the umbrella of Topics in Environmental Studies that will feature a campus community read of the 2009 book
Taking a page from Freshman Studies, Green Roots is sponsoring a special 1-unit course for Term III under the umbrella of Topics in Environmental Studies that will feature a campus community read of the 2009 book